What is LEAN Management? In any industry, minor improvements in innovation or production can have a major impact on profits. In such a fast-paced, competitive world, business owners always attempt to look for an edge in every element of their business, whether through improving product quality, lowering costs or shortening its supply chain lead time. Lean management appears as a business model that can help organisations attain these goals sustainably.
What is LEAN Management?
Lean, also known as “lean manufacturing” or “lean management”, is an approach that aims to reduce waste while maximising value for customers. The history of it begins with the automotive industry in the early 1920s as Henry Ford started the path to lean management with the Model T. Since then, Lean has spread worldwide to a wide variety of industries and companies.
At its core, Lean is about embracing efficient technology usage and designing all of a company’s processes and resources to focus on creating value for the customers. Their practices eliminate costs by achieving error-free production, minimising time and resources waste. Lean can help identify inefficiencies and implement improved workflows, helping leaders regulate production lines, make steady progress and monitor key performance indicators.

Principles of Lean Management
Since its existence, there have been numerous books, publications and reference websites defining LEAN principles or Lean pillars. The best known and established ones include the “Value Stream Mapping”, “TPS House” diagram, the “Lean thinking” in “Toyota Way 2001”, and “The Toyota Way: 14 Management Principles from the World’s Greatest Manufacturer” by Jeffrey K. Liker.
Although all of these principles from these different research are interesting and not necessarily one is better than the other, it seems like the “Value Stream” principle is often considered the most popular and wide-spread as the number of principles are reduced in order to be easily communicated and they are general enough not to be confined to a restrictive and underdeveloped model.
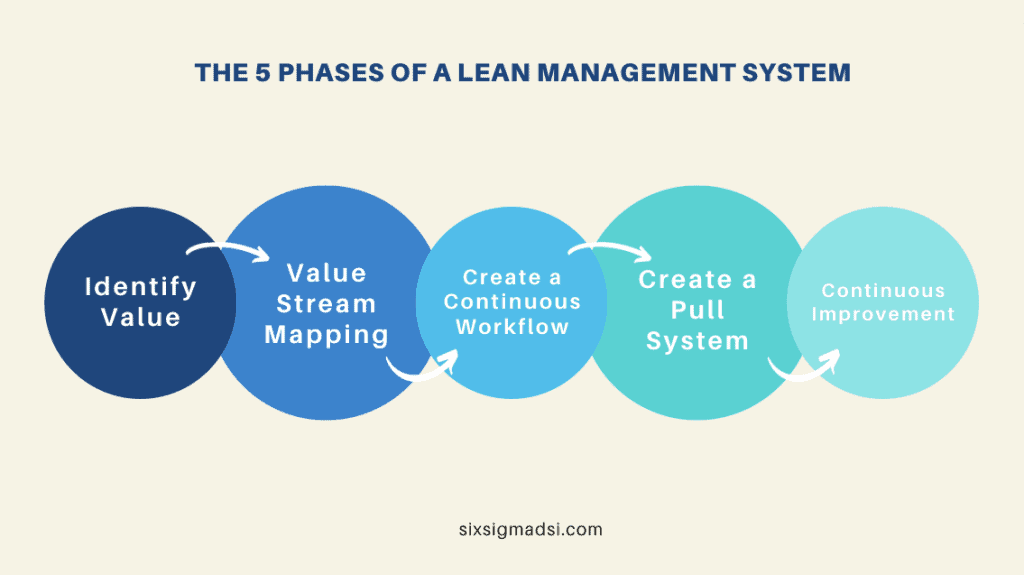
The “Value Stream Mapping” follows 5 core principles:
Identify Value
The value of your offering often lies in your company’s ability to address customer’s concern. Any activity that does not add value to the end product is considered waste. Thus, the very first principle is to clearly identify and define the value you want to bring to your offering. Once this is done, you’re ready to move on to the second principle of mapping the value chain workflow of your business.
Map the Value Chain
Your value chain flow should include all actions and people involved in delivering the end product to the customer. Applying this principle will allow you to identify unnecessary steps in the process and easily eliminate steps that do not add value
Create a Continuous Workflow
Once your value chain is handled, you will need to make sure that the workflow of each team runs smoothly. Bottlenecks and interruptions can happen anytime, therefore, breaking down tasks into smaller chunks and visualising the workflow can be two effective methods to conveniently detect and overcome any obstacles within the process.
Create a Traction System
Although a stable workflow helps you complete tasks quicker with much less effort, care still needs to be taken to create a traction system. In this system, work is only produced when there is demand. The capacity of the resources, as a result, is optimised: they are only mobilised when there is a real need.
Continuous Improvement
Once you have completed all the steps above, you’ve built your Lean management system. However, you need to remember that your system is not static, meaning that problems can arise with any of the previous steps. This is why there are different techniques to encourage continuous improvement, e.g. holding daily meeting to discuss any obstacles and solutions to those.
Benefits of LEAN Management
Cost Reduction
Lean management is all about maximising profits. Its practices aim to reduce waste in all forms so that all savings can be added to profit.
Improved Customer Interaction
With the customer’s viewpoint at the core, the way they address customer’s concerns is one of the leading drivers of cutting waste. Customer interactions and overall service, therefore, should improve.
Increased Quality
Lean management pays great attention to details with the goal of decreasing the number of defects and reworks in products. It means that processes will be optimised to avoid mistakes, leading to improvement in the quality of products and services.
Increased Employee Morale
Organisations with lean management often requires managers to regularly communicate with employees to improve work and process. As a result, employees could feel they are empowered and trusted to suggest improvements and take responsibility for their work. This results in a positive work environment and increased employee morale
Shorter Lead Time
By streaming processes and ensuring the smooth workflows, Lean makes it possible to shorten lead times from order to delivery, leading to faster deliveries to customers and quicker response to changing market conditions.

Disadvantages of LEAN Management
Like any other management methodology, Lean is not free from challenges. Some real disadvantages are associated with the Lean approach, including:
Time and resources required
Lean implementation takes a great deal of investment in terms of time and resources. Extensive employee training, process redesign, technology upgrades and organisational structure changes, just to name a few.
Complexity of implementation and maintenance
An effective and successful implementation of Lean needs a deep, thorough understanding of its principle and careful execution, which can be complex and challenging.
Cultural Challenges
Moving to a lean culture requires a huge change in mindset and broad acceptance within the organisation. Business owners might find an enormous number of employees who prefer traditional practices and have resistance to change, which can make implementation difficult.
Not Suitable for All Industries
Lean principles have its roots in manufacturing, therefore, it may not be directly applicable in certain service-oriented or creative sectors.

In Summary
Lean management is a powerful management philosophy that holds great potential in transforming organisations. It is not just about cutting costs – it values continuous improvement and respect for all people involved. To be effective, it must be well understood, communicated, supported and adapted to the specific needs of each organisation. A successful Lean implementation would require employee training and education not only on its tools and techniques but also on its core principles and philosophy. Overall, when applied correctly, a Lean management system can create a solid production system that significantly improves a company’s performance.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is lean management at its core?
Lean management, also known as “lean manufacturing” or “lean”, is an approach that aims to reduce waste while maximising value for customers. At its core, Lean is about designing all of a company’s processes and resources to focus on creating value for the customers. Their practices eliminate costs by achieving error-free production, minimising time and resources waste.
What is lean management and its benefits?
Lean management, often simply referred to as “lean manufacturing” or “lean”, is an approach that aims to reduce waste while maximising value for customers. Its benefits include increased efficiency, cost reduction, improved quality, better customer satisfaction, increased employee morale, and shorter lead time.
What is lean management principle?
Lean management principles, as described as “Value Stream Mapping”, follows five core principles: Identify value, Map the value chain, Create a continuous workflow, Create a traction system, and Continuous improvement. These principles guide organisations in optimising processes, fostering a positive work culture, and making decisions that contribute to shared goals and sustained success.




